- Visibility 430 Views
- Downloads 103 Downloads
- Permissions
- DOI 10.18231/j.ijnmhs.2021.006
-
CrossMark
- Citation
Fad diets on metabolic syndrome among sedentary women— A systemic review
- Author Details:
-
Swapan Banerjee *
Abstract
Introduction: Current trends show that many people, mainly young generations, are inclined to crash dieting by adopting various fad diets visible in popular search engines. Fad diets may be helpful in very few cases if customized for a particular patient or a person. As per current topics, metabolic syndrome is a severe issue that may be a single disorder or a group of diseases that often affect many people.
Objective: To systematically review and analyze current literature trends on various fad diets and their links with adult populations' metabolic syndrome.
Materials and Methods: A systemic review was conducted by searching and selecting open-sourced articles in Medline, EMBASE, SCI, Cochrane databases. Free text search and selective vocabulary terms relating to fad diets, crash dieting,weight-loss diet,metabolic syndrome diets, health,etc., were used for an online search. After extensive literature search and filtration of studies, finally, 13 studies were selected for the systemic review with the help of NVIVO 10 software.
Results: 'Word frequency'under the query section was used to analyze word frequency as per criteria. The searching text option was considered at the 40% level by choosing the 20 most frequent display words with five minimum lengths. The study showed the most focussing word 'weight' with 0.55% and 716 counts followed by 'health' with 0.41% having 620 counts in the word frequency list among all the 20 most used keywords in all the papers. Similarly, the word 'diet' was used in 561 counts with 0.43%. The study also demonstrated word cloud figure and cluster analysis by word similarity. Hence there was no need for other coding and meta-analysis as all papers were imported from Mendeley for review
Conclusion: More research is needed on the fad diet and metabolic syndrome; however, authors are concerned about public health safety.
Introduction
Fad diets or crash diets are becoming popular day by day, expecting quick weight loss and subsequent health benefits from other lifestyle disorders. Obesity is one of the significant burning issues that has increased three times in the last three decades (1.9 billion reported in 2016 by WHO). Simultaneously more than 35 million children have been reported as obese as per the record available from WHO [1], [2] The extreme diets, also called fad diets, have been practiced by many populations, mainly in metro cities and urban areas. The quick loss of weight by the improper and unscientific ways without calculative diet plans are often a cause of serious health hazard in various countries including India. The fad diets may reduce weight within a short time, but it comes back its position if discontinued. The fad diets somehow minimize weight, but the respective person often faces some health complications. [3] Commonly, they are weakness, hypoglycemia, hypo tension, hypovitaminosis, and other nutrients deficiencies. Sometimes, a concerned obese person may face many troubles to get back the lost health in total. [4], [5] Young girls and middle-aged women are another population group highly affected by obesity and crash dieting. The polycystic ovarian syndrome is one of the pervasive endocrine disorders among obese women,mainly resing in cities. Many studies showed that dyslipidemia is significantly correlated with PCOS women who always showed higher triglycerides and lower high-density lipoprotein cholesterol. [6] So metabolic disorders happen due to their improper lifestyles that can be compensated with proper diet and daily exercise for some time. In western countries like America and Europe, almost 28% of obese women are positively correlated with PCODin addition to type II diabetes. India is another prominent example undoubtedly. [7], [8], [9], [10], [11], [12] In general, Metabolic syndrome (MetS) is a group of metabolic disorders that include central obesity, hypertension, diabetes, dyslipidemia, atherosclerotic or non-atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases. [9], [10], [11], [12], [13]
Material And Methods
The systemic review was conducted searching foropen-sourced and open access articles in Medline, EMBASE, Sciences Citation Index, Cochrane database. Free text search and controlled vocabulary terms relating to fad diets, crash dieting diet diets on metabolic syndrome, exercise using OR, AND, NOT Boolean operators were applied as search methods. [9], [10], [11], [12], [13], [14], [15], [16], [17], [18] The 'similar article title and the 'related articles' were used to search from Google Scholar to locate more important additional articles. The citations' trackingwas done from Web of Science and Scopus' reference lists as per open access possibilities.
Inclusion criteria: All peer-reviewed papers published since 2020 in English were qualitatively identified and assessed in the perspective of various fad diets application on metabolic syndrome, highlighting mainly obesity, PCOS, and Cardiovascular disorders (mixed methods studies). The trending crash diet or so-called fad diets considered only. [8], [9], [10], [11], [12], [13], [14], [15], [16], [17], [18]
Exclusion criteria: The articles were excluded based on keyword search and precisely researched obesity, PCOD, and cardiovascular diseases. Further, adult populations had been considered only but not children. The diet patterns which are scientifically proven already not included as these are not our discussion.
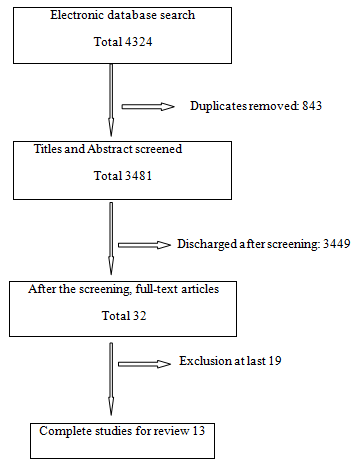
Screening of data
A total of 4324 articles were searched in the various electronic database, including scholarly articles in Google as search engines. Total 3481 articles came into the shortlist after the removal of 843 duplicates articles at the primary level. A whole 3449 numbers of articles were discharged and finally selected 32 with full papers based on inclusion and exclusion criteria by following the relevant keywords. At last, 13 complete studies were finally selected in this review study divided into 3 tables by reviewing the following health issues such as i) Obesity, ii) PCOS & iii) Cardiovascular disorders. [18], [19]
Extraction of data
NVivo 10 as software has been used for data screening and data analysis. All 32 articles were uploaded as pdf versions in Mendeley, followed by exporting into the computer's'my collection' (RIS formatted file). The 'my collection' file was uploaded to analyze the studies. [18], [20], [15]
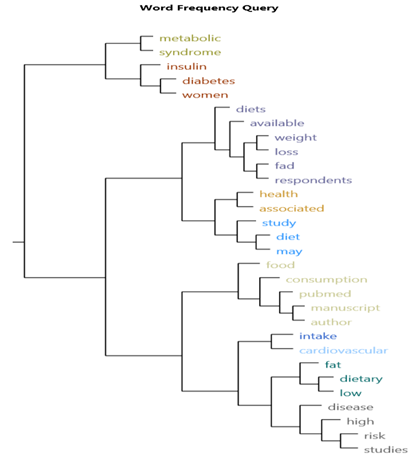
Word frequency under the query section was used to analyze word frequency as per frequency criteria by searching text option at the 40% level of search by choosing 20 most frequent display words with 5 minimum length. A total summary of all 20 words has been noted in a table with their percentage position irrespective of uses in the papers as keywords (ref: table.2).The words cloud image has been considered and showed here for better understanding ( fig-2). A cluster analysis of all 13 papers has also been done, and the figures have been guiding here in this article (fig.3).
Fad diet, Diet patterns, Health; Associations, Weight management; Energy intake; High-fat diet; Leptin; Metabolic syndrome; Diet; Exercise; Metabolic syndrome; Cancer; Coronary artery disease; Diabetes; Hypertension; Metabolic syndrome; Crash diet.
Results
The systemic review study sorted and finally selected 13 research articles that were 12 in 'internals' 1 in 'externals' under the part of 'sources.' In addition to that, memos were attached in the same position. Still, the memos were not included for analysis. Hence, the articles uploaded in Internal Sources have illustrated the total picture of the reference chart mentioning all authors' categories irrespective of the articles' publications details. In this review study, the final inclusions were the year of publication, name of titles of the individual articles, and their volume, issue, pages, section, and a secondary title, if any. (ref: table.1). The analysis has been done in three parts which concerned all types of fad diet and various diseases. Secondly, the importance of diet and exercises focusing on crash dieting effects. Lastly also the papers related to cardiovascular diseases and types of diet applied.
The study analyzed the primary 20 keywords that were used in the selected papers in the reference list. Out of which, weight as a word got maximum weight age that showed 0.55% with 716 counts followed by 0.41% with 620 counts in the word frequency list among all the 20 most used keywords in all the papers. Similarly, the word 'diet' was used in 561 counts with 0.43%. I have only demonstrated word frequency at 20 words search level and cluster analysis by word similarity in the paper. Hence, there was no need for other coding and meta-analysis (table.2. & fig.4).
1 showed the complete list of all articles finally selected. All the papers discussed the various trending fad diets or crash dieting often used worldwide based on their literature survey. From 2005 till 2020, as current years sorted and selected articles were considered for this systemic review. In case no data then noted as unassigned.
The above table demonstrated and reviewed all the related keywords frequently observed in the 13 studies. The words were focused as per study perspectives with the percentage, count, and length. Therefore, fad diets highly matter with weight, obesity, cardiovascular diseases, and overall metabolic syndromes as per the author's work since 2005. At the same time, figure 2 and figure 3 demonstrated word cloud and word frequency flow consecutively, focusing on the most used keywords for current and future research
The above graph was prepared based on authors' perceptions and subsequently their year-wise work. Hence various research cum reviews were published in the perspective of fad diets' proper application.
|
Year |
Author |
Title |
Volume |
Issue |
Pages |
Secondary Title |
Section |
|
2005 |
Roberts, Christian K.; Barnard, R. James |
Effects of exercise and diet on chronic disease |
98 |
1 |
3 - 30 |
Journal of Applied Physiology |
3 |
|
2006 |
Ignatius G.E. Zarraga, MD; Ernst R. Schwarz. |
Impact of Dietary Patterns and Interventions on Cardiovascular Health |
114 |
9 |
961 - 973 |
Contemporary Reviews in Cardiovascular Medicine Cardiovascular Health |
961 |
|
2006 |
Pitsavos, Christos; Panagiotakos, Demosthenes; Weinem, Michael; Stefanadis, Christodoulos |
Diet, Exercise and the Metabolic Syndrome |
3 |
3 |
118 - 118 |
The Review of Diabetic Studies |
118 |
|
2007 |
Pekhlivanov, B.; Kaleva-Khodzheva, N.; Orbetsova, M.; Mitkov, M. |
Metabolic syndrome in women with polycystic ovary syndrome |
46 |
9 |
37 - 40 |
Akusherstvo i ginekologiia |
37 |
|
2007 |
Rasouli, Parsa; Lu, Xiangyi; |
Potential Long-Term Consequences of Fad Diets on Health, Cancer, and Longevity: Lessons Learned from Model Organism Studies |
6 |
2 |
247-253 |
Technology in Cancer Research and Treatment |
247 |
|
2013 |
García Reyes, Luis Enrique |
Exposure To Fad Diet Advertising Among Youth And Young Adults In Canada |
53 |
9 |
1689 - 1699 |
Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling |
1689 |
|
2016 |
Daulatabad, Deepashree; Grover, Chander; Singal, Archana |
Quality of life and psychological impact of premature canities: A study from North India |
3 |
1 |
24 - 28 |
Pigment International |
24 |
|
2016 |
Anand, Sonia S; Hawkes, Corinna; Souza, Russell J De; Mente, Andrew; Nugent, Rachel; Zulyniak, Michael A; Weis, Tony; Bernstein, Adam M; Kromhout, Daan; Jenkins, David J A; Malik, Vasanti; Martinez-, Miguel A |
Food Consumption and its Impact on Cardiovascular Disease: Importance of Solutions Focused on the globalized food system: |
66 |
14 |
1590 - 1614 |
Journal of t h e American College of Cardiology |
1590 |
|
2016 |
Pitt, Christopher E. |
Cutting through the Paleo hype: The evidence for the Palaeolithic diet |
45 |
1 |
35 - 38 |
Australian Family Physician |
35 |
|
2018 |
Blanton, Jarad |
Implications of the Ketogenic Diet on Metabolic Syndrome |
1 |
NA |
1-28 |
Eastern Illinois University |
1 |
|
2019 |
Yu, Edward; Malik, Vasanti S; Hu, Frank B |
Cardiovascular Disease Prevention by Diet Modification |
72 |
8 |
914 - 926 |
Journal of t h e American College of Cardiology |
914 |
|
2019 |
Greaves, Colin Poltawski, Leon Garside, Ruth Briscoe, Simon |
Understanding the challenge of weight loss maintenance: a systematic review and synthesis of qualitative research on weight loss maintenance |
11 |
2 |
145-163 |
Health Psychology Review |
145 |
|
2020 |
Barbosa, Claudiane Maria; Figueiredo, Vivian Paulino; Barbosa, Maria Andréa; Cardoso, Leonardo Máximo; Alzamora, Andréia Carvalho; Cardoso, Leonardo Máximo; Alzamora, Andréia Carvalho |
Maternal high-fat diet triggers metabolic syndrome disorders that are transferred to first and second offspring generations |
123 |
1 |
59 - 71 |
British Journal of Nutrition |
59 |
|
Word |
Length |
Count |
Weighted percentage (%) |
|
Associated |
10 |
317 |
0.25 |
|
Author |
6 |
337 |
0.26 |
|
Available |
9 |
324 |
0.25 |
|
Cardiovascular |
14 |
316 |
0.24 |
|
Consumption |
11 |
308 |
0.24 |
|
Diabetes |
8 |
416 |
0.32 |
|
Dietary |
7 |
524 |
0.41 |
|
3.Diets |
5 |
561 |
0.43 |
|
Disease |
7 |
515 |
0.40 |
|
2.Health |
6 |
620 |
0.48 |
|
Insulin |
7 |
312 |
0.24 |
|
Intake |
6 |
361 |
0.28 |
|
Manuscript |
10 |
338 |
0.26 |
|
Metabolic |
9 |
392 |
0.30 |
|
Pubmed |
6 |
381 |
0.30 |
|
Studies |
7 |
362 |
0.28 |
|
Study |
5 |
484 |
0.37 |
|
Syndrome |
8 |
390 |
0.30 |
|
1.Weight |
6 |
716 |
0.55 |
|
Women |
5 |
342 |
0.26 |
.


|
Reference Type |
Author |
Year |
Title |
Publisher |
Volume |
Issue No. |
Pages |
Section |
|
Journal Article |
Barbosa et al. |
2020 |
Maternal high-fat diet triggers metabolic syndrome disorders that are transferred to first and second offspring generations |
British Journal of Nutrition |
123 |
1 |
59 - 71 |
59 |
|
Journal Article |
Blanton, Jarad |
2018 |
Implications of the Ketogenic Diet on Metabolic Syndrome |
Eastern Illinois University |
1 |
1 |
1-29 |
1 |
|
Pitsavos, et.al |
2006 |
Diet, Exercise and the Metabolic Syndrome |
The Review of Diabetic Studies |
3 |
3 |
118 - 118 |
118 |
|
|
Journal Article |
Pitt, Christopher E. |
2016 |
Cutting through the Paleo hype: The evidence for the Palaeolithic diet |
Australian Family Physician |
45 |
1 |
35 - 38 |
35 |
|
Reference Type |
Author |
Year |
Title |
Publisher |
Volume |
Issue No. |
Pages |
Section |
|
Journal Article |
Daulatabad et al. |
2016 |
Quality of life and psychological impact of premature canities: A study from North India |
Pigment International |
3 |
1 |
24-28 |
24 |
|
Journal Article |
García Reyes, Luis Enrique |
2013 |
Exposure To Fad Diet Advertising Among Youth And Young Adults In Canada |
Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling |
53 |
9 |
1689 - 1699 |
1689 |
|
Journal Article |
Pekhlivanov et al. |
2007 |
Metabolic syndrome in women with polycystic ovary syndrome |
Akusherstvo i ginekologiia |
46 |
9 |
37-40 |
37 |
|
Journal Article |
Roberts, Christian K.; Barnard, R. James |
2005 |
Effects of exercise and diet on chronic disease |
Journal of Applied Physiology |
98 |
1 |
3 - 30 |
3 |
|
Reference Type |
Author |
Year |
Title |
Publisher |
Volume |
Issue No. |
Pages |
Section |
|
Journal Article |
Yu, Edward; Malik, Vasanti S; Hu, Frank B |
2019 |
Cardiovascular Disease Prevention by Diet Modification |
Journal of t h e American College of Cardiology |
72 |
8 |
914-926 |
914 |
|
Journal Article |
Ignatius G.E. Zarraga, MD; Ernst R. Schwarz. |
2006 |
Impact of Dietary Patterns and Interventions on Cardiovascular Health |
Contemporary Reviews in Cardiovascular Medicine Cardiovascular Health |
114 |
9 |
961-973 |
961 |
|
Journal Article |
Anand et al., |
2016 |
Food Consumption and its Impact on Cardiovascular Disease: Importance of Solutions Focused on the globalized food system: |
Journal of t h e American College of Cardiology |
66 |
14 |
1590 - 1614 |
1590 |
|
Journal Article |
Rasouli, Parsa; Lu, Xiangyi; |
2007 |
Potential Long-Term Consequences of Fad Diets on Health, Cancer, and Longevity: Lessons Learned from Model Organism Studies |
Technology in Cancer Research and Treatment |
6 |
2 |
247-253 |
247 |
Discussion
As per analyzing 13 research articles, 20 keywords were mainly highlighted based on a maximum of 14 lengths and a minimum of 5 lengths. The 'weight' is visible as a mostly focussed word due to the full implementation of fad diet on weight management by the ordinary people considering an instant response. As per word frequency query results,weight was mainly visible, followed by health and diet. This denotes that studies in the subject of weight management and fad diet, the two keywords primarily used in search engines and other databases.
The word cloud also depicted that fad diets are often discussed for weight management among women worldwide. The point was further strengthened by the cluster analysis that authors are concerned with the work type by references irrespective of attribute values. [25], [26], [27] The review study was the done for the well-being of the society who are directly or indirectly not aware of the proper uses of diet plan. However, other important factors such as social awareness advise to practise yoga and other exercises to cope with syndromes such as hypothyroidism, poly cystic ovarian syndrome, diabetes, and different lifestyle diseases. [25], [26], [27], [28]
Conclusion
The systemic review study is essential for a severe issue like crash dieting practices through various unscientific fad diets for instant weight loss or metabolic syndrome. As scientists or medical professionals, authors are currently highly concerned about public health safety towards fad diets. The reason is they are not often customized or following respective published dietary or other medical guidelines. More research is required to understand the fad diets' safe and unsafe parts for metabolic syndrome.
Source of Funding
None.
Conflict of Interest
None .
References
- Mohan V, Joshi S. Pros & cons of some popular extreme weight-loss diets. Indian J Med Res. 2018;148(5):642-47. [Google Scholar]
- . Obesity and overweight. World Health Organisation. 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zarraga GE, Schwarz ER. Impact of Dietary Patterns and Interventions on Cardiovascular Health. Circulation. 2006;114(9):961-73. [Google Scholar]
- Dansinger ML, Gleason JA, Griffith JL, Selker HP, Schaefer EJ. Comparison of the Atkins, Ornish, Weight Watchers, and Zone Diets for Weight Loss and Heart Disease Risk Reduction. JAMA. 2005;293(1):43-53. [Google Scholar]
- Mohan V, Radhika G, Sathya RM, Tamil SR, Ganesan A, Sudha V. Dietary carbohydrates, glycaemic load, food groups and newly detected type 2 diabetes among urban Asian Indian population in Chennai, India (Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study 59). Br J Nutr. 2009;102(10):1498-506. [Google Scholar]
- Ganie MA, Kalra S. Polycystic ovary syndrome - A metabolic malady, the mother of all lifestyle disorders in women - Can Indian health budget tackle it in future?. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2011;15(4):239-41. [Google Scholar]
- Azziz R, Woods KS, Reyna R, Key TJ, Knochenhauer ES, Yildiz BO. The Prevalence and Features of the Polycystic Ovary Syndrome in an Unselected Population. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004;89(6):2745-9. [Google Scholar]
- Rochlani Y, Pothineni NV, Kovelamudi S, Mehta JL. Metabolic syndrome: pathophysiology, management, and modulation by natural compounds. Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis. 2017;11(8):215-25. [Google Scholar]
- Greaves C, Poltawski L, Garside R, Briscoe S. Understanding the challenge of weight loss maintenance: a systematic review and synthesis of qualitative research on weight loss maintenance. Health Psychol Rev. 2017;11(2):145-63. [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee S. Implementation of the vegan diet among obese hypothyroid housewives living in metro cities - A review. Res J Med Sci. 2020;8(1):21-25. [Google Scholar]
- Connolly J. Effects of dieting and exercise on resting metabolic rate and implications for weight management. Fam Pract. 1999;16(2):196-201. [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee S, Srivastava S. Disease & Diet: A handbook on home-based dietary. . 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts CK, Barnard RJ. Effects of exercise and diet on chronic disease. J Appl Physiol. 2005;98(1):3-30. [Google Scholar]
- Zarraga IGE, Schwarz ER. Impact of Dietary Patterns and Interventions on Cardiovascular Health. Circ. 2006;114(9):961-73. [Google Scholar]
- Pitsavos C, Panagiotakos D, Weinem M, Stefanadis C. Diet, Exercise and the Metabolic Syndrome. Rev Diabet Stud. 2006;3(3):118-26. [Google Scholar]
- Pekhlivanov B, Khodzheva N, Orbetsova M, Mitkov MP. Potential Long-Term Consequences of Fad Diets on Health, Cancer, and Longevity : Lessons Learned from Model Organism Studies. Akush Ginekol . 2007;46(9):37-40. [Google Scholar]
- Reyes LG. Exposure To Fad Diet Advertising Among Youth And Young Adults In Canada. J Chem Inf Model. 2013;53(9):1689-99. [Google Scholar]
- Daulatabad D, Grover C, Singal A. Quality of life and psychological impact of premature canities: A study from North India. Eye. 20161;3:24-32. [Google Scholar]
- Anand SS, Hawkes C, Souza RJ, De, Mente A, Nugent R. Food Consumption and its Impact on Cardiovascular Disease: Importance of Solutions Focused on the globalized food system. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016;66(14):1590-614. [Google Scholar]
- Pitt CE. Cutting through the Paleo hype: The evidence for the Palaeolithic diet. Aust Fam Physician. 2016;45(1):35-8. [Google Scholar]
- Blanton J. Implications of the Ketogenic Diet on Metabolic Syndrome. . 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yu E, Malik VS, Hu FB. Cardiovascular Disease Prevention by Diet Modification. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018;72(8):914-26. [Google Scholar]
- Greaves C, Poltawski L, Garside R, Briscoe S. Understanding the challenge of weight loss maintenance: a systematic review and synthesis of qualitative research on weight loss maintenance. Health Psychol Rev. 2017;11(2):145-63. [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa CM, Figueiredo VP, Barbosa MA, Cardoso LM, Alzamora AC. Maternal high-fat diet triggers metabolic syndrome disorders that are transferred to first and second offspring generations. Br J Nutr. 2020;123(1):59-71. [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee S. Study on Yoga Intervention along with Diet on Hypothyroidism Associated with Obesity among Sedentary Working Women in West Bengal. Int J Yoga Allied Sci. 2019;8(1):18-23. [Google Scholar]
- Lakka TA, Laaksonen DE. Physical activity in prevention and treatment of the metabolic syndrome. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2007;32(1):76-88. [Google Scholar]
- Iwen KA, Schröder E, Brabant G. Thyroid Hormones and the Metabolic Syndrome. Eur Thyroid J. 2013;2(2):83-92. [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee S. Role of Food Companies to Supply Nutritious Foods as per Buyers Changing Lifestyles, Buying Habits and the Recent Trends. Int J Innov Res Sci Eng Technol. 2020;9(3):1062-7. [Google Scholar]
How to Cite This Article
Vancouver
Banerjee S. Fad diets on metabolic syndrome among sedentary women— A systemic review [Internet]. J Nutr Metab Health Sci. 2021 [cited 2025 Nov 09];4(1):34-40. Available from: https://doi.org/10.18231/j.ijnmhs.2021.006
APA
Banerjee, S. (2021). Fad diets on metabolic syndrome among sedentary women— A systemic review. J Nutr Metab Health Sci, 4(1), 34-40. https://doi.org/10.18231/j.ijnmhs.2021.006
MLA
Banerjee, Swapan. "Fad diets on metabolic syndrome among sedentary women— A systemic review." J Nutr Metab Health Sci, vol. 4, no. 1, 2021, pp. 34-40. https://doi.org/10.18231/j.ijnmhs.2021.006
Chicago
Banerjee, S.. "Fad diets on metabolic syndrome among sedentary women— A systemic review." J Nutr Metab Health Sci 4, no. 1 (2021): 34-40. https://doi.org/10.18231/j.ijnmhs.2021.006
